Atrial Fibrillation
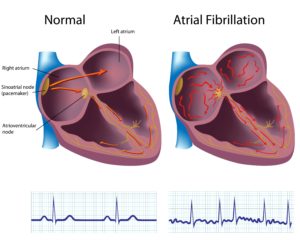 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) causes the heart’s two upper chambers to beat irregularly and too fast. Typically, small cells give off electric signals that cause the heart to beat steadily. An electrocardiogram (ECG) can measure if the signals are elevated or are within a normal range.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) causes the heart’s two upper chambers to beat irregularly and too fast. Typically, small cells give off electric signals that cause the heart to beat steadily. An electrocardiogram (ECG) can measure if the signals are elevated or are within a normal range.
CAUSES
Damage to the structure of the heart is the most common cause of arterial fibrillation.
The following conditions can cause AFib:
- Heart attack
- Increased blood pressure
- Irregular heart valves
- Coronary artery disease
- Metabolic imbalance
- Congenital heart defects
- Pacemaker malfunction
- Stimulants (caffeine, alcohol, tobacco)
- Prior heart surgery
- Lung disease
- Sleep apnea
- Viral infection
- Stress
SYMPTOMS
Signs and symptoms of arterial fibrillation include:
- Sweating, dizziness, and pressure or pain in the chest
- Rapid and irregular heartbeat
- Rapid heartbeat or beating in the chest
- Anxiety and shortness of breath
- Fainting
- Fatigue easily when exercising
*Stock photographs and artwork are for illustrative purposes only. This article contains general information about medical conditions and treatments. The information is not advice, and should not be treated as such. You must not rely on this article as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or other healthcare providers.





